- Data introduction
- Form of data
Data can be mainly divided into two forms, that is, the usual way of data expression, which can also be called the data carrier.
Electronic data: stored in hard disk and other storage devices, or stored in application database, which can only be read by computer, U disk or application program. For example: customer information in the database.
Paper data: the data is intuitively presented on the carrier in the form of paper. For example: insurance policy, application form, etc.
- Data storage mode
Data is everywhere and permeates every field of our work and life. The common data storage methods include: network storage server: for example, DAS, NAS, San, etc; cloud storage; Mobile devices: mobile phones, tablets, and devices supporting wireless applications, etc; Paper documents. With Vinchin Backup & Recovery, you can easily recover XenServer VM in a straightforward way.
- Data lifecycle
Data has a complete life cycle from the initial generation to the destruction of data. At this time, enterprises need to protect different types of data at each stage of the data life cycle. The most common method is to formulate information classification policies.
For example:
According to the conventional sense, the data can be divided into four categories: open, internal, confidential and highly confidential. Each type of data is becoming more and more sensitive from open to highly confidential, which is the standard of information classification.
Enterprises need to formulate information classification policies, so that the data owner has the right to define what kind of data the currently owned data belongs to, and formulate information classification protection matrix according to the classification policies. Vinchin will simultaneously encrypt your RHV backups when they’re transferred to the backup repository.
The information classification protection matrix is similar to excel in that it needs rows and columns. Taking the above classification standards as an example, an enterprise divides data into four types. These four types of data are the four columns in Excel. Each row is the life cycle of the data. The cells where rows and columns intersect are the data protection requirements for the classified data in the current data life cycle stage. This excel forms the information classification protection matrix.
- Value of data
Any data is valuable. For companies, banks and other similar financial institutions, as long as a piece of customer information is leaked and exposed by the media, it will cause great risks to the company, such as regulatory risk, financial risk and reputation risk. Therefore, confidential data, such as customer information and the company’s financial statements, are vital to the enterprise and the lifeblood of the enterprise.
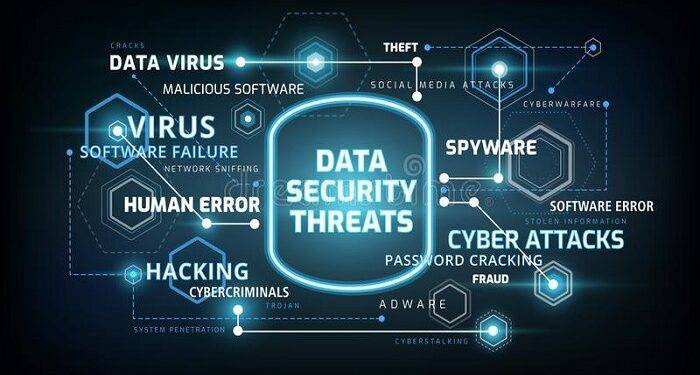
- Data security threats and risks
Information security has three basic characteristics: availability, integrity and confidentiality. Availability means that data can be obtained and available at any time, and data cannot be read due to hardware failure and other problems. Integrity means that the data is not subject to malicious tampering and unauthorized access during the whole transaction process to ensure that the data is the original. Confidentiality means that the data is encrypted in the whole process, will not be eavesdropped, and will not be accessed by unauthorized people. The data is safe. The information security protection we usually talk about is to protect the three most basic characteristics of data.
- Data availability threats and risks
Malicious software threats, extortion software viruses, worms, logic bombs and other power failures, server failures, hardware failures, hard disk damage, user error deletion, and no backup files.
- Data integrity threats and risks
The threat of malicious software, such as Trojan horse files and other virus files. Users delete application vulnerabilities by mistake. 3. Data confidentiality threats and risks.
Malware threats, such as spyware, Trojan horse and Keylogger; Unauthorized access due to loss of disk or other data storage devices; Internal personnel intentionally disclose confidential data; Social worker attacks to obtain important data through deception and counterfeiting, for example: password information 4. Data compliance risk.
The legal and regulatory authorities have clear requirements for the collection, storage, use and transmission of data. The company will suffer financial loss and reputation loss if it fails to comply with the provisions of the law and regulation on data. Therefore, the company also needs to formulate data security protection standards, and needs to conduct safety awareness training for employees in combination with such standards, so that employees can strictly abide by them.
III. Data security protection measures
Management control refers to administrative laws and regulations and administrative means of the company. Technical control, also known as logical control, refers to safety protection directly through technical means. Physical control refers to the control related to physical safety.
- Management control
Formulate data security related strategies and standards: information classification standards, information classification protection matrix, electronic data use security standards, carry out data security awareness training for employees, correctly guide employees to properly handle data, and security professionals must review all relevant laws and regulations and check their applicability to the enterprise. The enterprise must obey the laws governing the use of data and systems, such as the general provisions of the civil law Network security law of the people’s Republic of China, etc. Data retention 2. Technical control.
1) Redundancy technology
In addition to the main resource sets of the computing environment, the attribute “one more” of one or more groups of additional resources is also reserved to avoid single point of failure. The redundancy technologies of the computer room such as power supply redundancy, server redundancy, website equipment redundancy, etc. for example, the redundancy of hot station, warm station and cold war hard disk, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10 and raid01.
2) Non sustainability
Once the computing environment completes the assigned task, it will be discarded to protect the integrity of the original data. VDI non persistent mode: changes will be lost after logging out, otherwise it will deviate from the security baseline.
3) Data backup
Full backup differential backup incremental backup data regular backup to prevent accidental loss of data, it is necessary to regularly check the effectiveness of data backup.
4) Encryption
Anti eavesdropping prevent unauthorized access after device loss protect the confidentiality of data through disk encryption, database encryption, file encryption, USB Encryption, email encryption and voice encryption use strong encryption algorithms, such as AES to encrypt and protect temporary session security through session key 5) identity access control.
Strict identity access control is implemented for key assets, such as two factor authentication and login exception monitoring through Siem 6) data destruction.
To delete, right-click “permanently delete” to simply remove the mark. The data is still on the disk. The demagnetization can be easily restored by the data recovery software. The strong magnetic force is applied to the disk drive to lose the magnetic charge, but it can also be re magnetized and eliminated. After deleting the data, the original data can be overwritten with new content repeatedly, the data can be completely removed or the system can be re divided, and the physical destruction can be removed, It is the most thorough data destruction method, including excision, powder extraction, incineration, etc.